 |
The History of Michigan
Michigan became a U.S. territory in 1805 and gained statehood in 1837 as the 26th state. Its growth was fueled by the fur trade, lumber industry, and later the rise of the automobile industry centered in Detroit. |
|
 |
Ojibwe (Chippewa) Nation
The Ojibwe, also known as Chippewa, are one of the largest Indigenous groups in North America, traditionally living around the Great Lakes region. They are known for their rich oral traditions, birchbark canoes, and skilled use of natural resources like wild rice. |
|
 |
Marquette and Joliet
Jacques Marquette and Louis Joliet were French explorers who, in 1673, led an expedition to explore the Mississippi River in search of the Northwest Passage. Though they discovered the river flowed south and not west to Asia, their journey provided valuable maps and opened the interior of North America to further French exploration. |
|
 |
The Explorations of Robert Sieur de la Salle
Robert Sieur de La Salle was a French explorer who claimed the entire Mississippi River Basin for France in 1682, naming it Louisiana. His ambitious expeditions expanded French influence in North America, though his final colonization attempt ended in disaster and his own death. |
|
 |
The Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory was a vast area of land in the early United States, stretching from the Great Lakes to the Ohio River and including parts of modern-day Ohio, Indiana, Indiana, Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota. It was gained after the British ceded it following the French and Indian War and eventually became the foundation for several new states.
|
|
 |
Pontiac's Rebellion
Pontiac's Rebellion was a war waged by Indians of the Great Lakes region against British rule after the French and Indian War. The Indians, who had formed alliances with the defeated French, were dissatisfied with treatment from British officials. |
|
 |
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, also known as the Seven Years War, began in the Spring in 1754. The dispute arose over the presence of British and French settlers in the Ohio River Valley (in and around present day Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania), but resulted in battles that were fought far from there. |
|
 |
Tecumseh's War
Tecumseh's War was a conflict in the early 1800s between a Native American confederation, led by Shawnee chief Tecumseh, and the United States, as Native tribes tried to resist American expansion into their lands. The war ended after Tecumseh’s death in 1813 during the War of 1812, weakening Native resistance in the Midwest. |
|
 |
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a conflict between the United States and Great Britain, sparked by issues like trade restrictions and the impressment of American sailors. It ended in 1815 with the Treaty of Ghent, restoring prewar boundaries but boosting American national pride. |
|
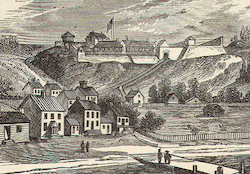 |
Battle of Fort Mackinac- July 17, 1812
The Battle of Mackinac took place in 1812 when British forces and Native American allies captured Fort Mackinac from a small American garrison without a fight. In 1814, American troops tried to retake the fort but failed due to strong British defenses on the island. |
|
 |
Battle of Dearborn- August 15, 1812
The Battle of Dearborn took place in August 1812 near present-day Chicago when Potowatomi warriors ambushed American evacuees from Fort Dearborn. Over half of the group, including women and children, were killed, and the fort was burned down, leaving the area under Native control until after the war. |
|
 |
Surrender of Fort Detroit - August 16, 1813
The Battle of Fort Detroit occurred on August 16, 1812, when U.S. General William Hull surrendered the fort to British General Isaac Brock without a fight. The British, with the help of Tecumseh and his warriors, used deception to appear stronger, leading to an early and embarrassing American defeat. |
|
 |
Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny was the 19th-century belief that the United States was destined by God to expand its territory across North America. It was used to justify westward expansion, the displacement of Native Americans, and wars such as the Mexican-American War. |
|
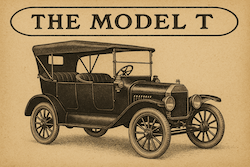 |
Henry Ford and the Rise of the Ford Motor Company
Henry Ford revolutionized transportation by founding the Ford Motor Company in 1903 and introducing the Model T in 1908. He pioneered the moving assembly line, making cars affordable for many Americans and transforming modern industry.
|
|