 |
The History of North Carolina
North Carolina, one of the original Thirteen Colonies, was first settled by Europeans in the late 1600s and became a center for tobacco and agriculture. It played a key role in the American Revolution and was the first state to call for independence from Britain in 1776. |
|
 |
Cherokee Nation
The Cherokee are one of the largest Native American tribes, originally inhabiting the southeastern United States, including parts of Georgia, Tennessee, and the Carolinas. Known for their sophisticated society, farming practices, and the creation of a written language by Sequoyah, the Cherokee were forcibly removed from their land in the 1830s during the Trail of Tears. |
|
 |
The Lost Colony of Roanoke Island
The Lost Colony of Roanoke was an English settlement established in 1587 on Roanoke Island, off the coast of present-day North Carolina. When supply ships returned in 1590, the colony had mysteriously vanished, leaving only the word “CROATOAN” carved into a post as a clue. |
|
 |
North Carolina Colony
The North Carolina Colony, originally part of the Province of Carolina, was established in 1663 and became a separate royal colony in 1712. Its economy was based on agriculture, particularly tobacco, rice, and indigo, and it was known for its independent spirit and resistance to British control.
|
|
 |
The North Carolina Economy
|
|
 |
Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) was a conflict between the thirteen American colonies and Great Britain, resulting in the colonies gaining independence. It began with growing tensions over British taxation and governance and ended with the Treaty of Paris, which recognized the United States as a sovereign nation. |
|
 |
Battle of Kings Mountain
The Battle of Kings Mountain, fought on October 7, 1780, was a decisive Patriot victory during the American Revolutionary War. Frontier militia defeated Loyalist forces in a brutal hillside fight, boosting American morale and turning the tide in the Southern campaign. |
|
 |
The Battle of Guilford Courthouse
The Battle of Guilford Courthouse, fought on March 15, 1781, was a costly British victory where General Cornwallis defeated Nathanael Greene’s larger army but suffered heavy losses, weakening British forces and setting the stage for their eventual surrender at Yorktown. |
|
 |
The Invention of the Cotton Gin
The invention of the cotton gin greatly increased the profitability of cotton farming, leading to a rapid expansion of slavery in the Southern states. This growth in slavery deepened the divide between the North and South, contributing to the tensions that eventually led to the Civil War. |
|
 |
Chickamauga Wars
The Chickamauga Wars were a series of battles, ambushes, and massacres staged between Cherokee forces under Dragging Canoe and the many militias comprised of Scotch-Irish settlers in Kentucky, the Carolinas, Tennessee, and Georgia during and after the Revolutionary War. |
|
 |
Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny was the belief that the United States was meant to expand westward across the continent. As new territories were added, fierce debates over whether slavery would be allowed in these areas increased tensions between the North and South, helping lead to the Civil War. |
|
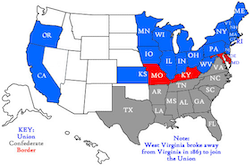 |
Secession of the Southern States
The secession of Southern states in 1860 and 1861, initiated by South Carolina, was a direct response to the election of Abraham Lincoln, whose anti-slavery stance threatened the institution central to the Southern economy and way of life. This collective withdrawal from the Union led to the formation of the Confederate States of America, setting the stage for the outbreak of the Civil War. |
|
 |
Civil War
The American Civil War (1861–1865) was fought between the Northern states (Union) and the Southern states that seceded to form the Confederacy, primarily over the issues of slavery and states’ rights. It resulted in the preservation of the Union and the abolition of slavery, but at the cost of over 600,000 lives. |
|
 |
Sherman's March to the Sea
Sherman's March to the Sea was a devastating Union campaign from Atlanta to Savannah, Georgia, in late 1864, led by General William T. Sherman. His troops destroyed railroads, crops, and infrastructure along the way to break the South's will to fight and cripple its ability to wage war.
|
|
 |
Reconstruction
Reconstruction after the Civil War (1865–1877) aimed to rebuild the South and integrate formerly enslaved people into American society with new rights, including citizenship and voting. In South Carolina, this period saw significant political participation by African Americans but also violent resistance and the rise of groups like the Ku Klux Klan, which ultimately undermined many of these gains. |
|
 |
The Wright Brothers and First Flight
The Wright Brothers, Orville and Wilbur, were American inventors who achieved the first powered, controlled flight in 1903 near Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Their innovations in aviation laid the foundation for modern airplane design and travel. |
|